New advancements in research are always taking place in the food industry, it can be tricky to keep up to date with the latest findings. Probiotics and fermented foods have been popular in the media lately, although they are not the same the difference between them is unknown to many.
What are probiotics?
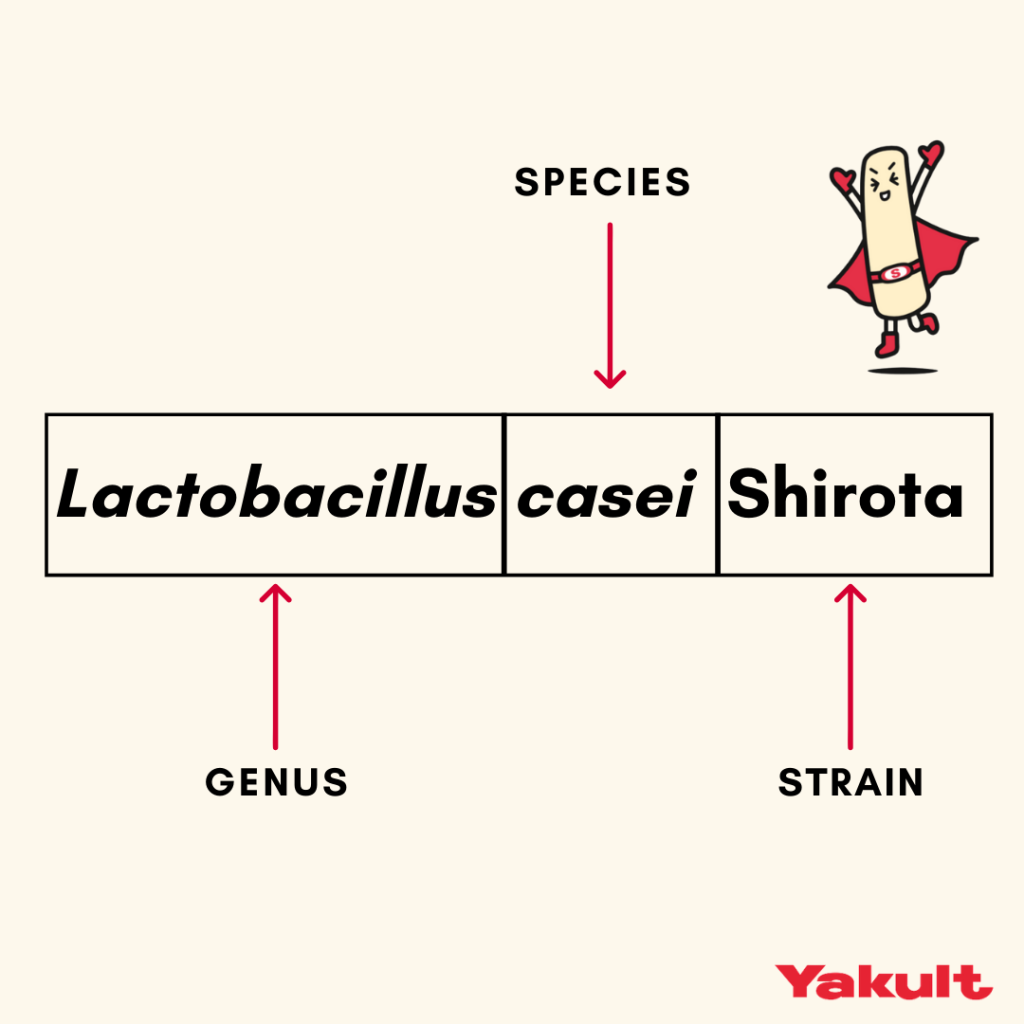
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. When we consume probiotics, they increase the number of beneficial bacteria already in out gut. Live microorganisms may be present in many foods and supplements, but a good quality probiotic will always display the 3-part name of their specific characterised strain like the image above.
There are multi-strain probiotic products containing more than one strain, but this does not make them more effective than a probiotic product with a single strain. Likewise, a probiotic supplement might contain a higher number of live bacteria per serve compared to another product, but this is not necessarily better as the quality of the strain takes precedence. Choose a probiotic from a reputable brand and check with the manufacturer to ensure it contains sufficient amounts of live bacteria per serve.
What are fermented foods?
International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) defines fermented foods as those made through desired microbial growth and enzymatic conversions of food components. Fermentation is a chemical change that occurs to food products brought about from microscopic yeast and bacteria. Fermenting foods is often done to improve the shelf stability of the foods and to add to the character or flavour of the food.
Examples are kefir, kombucha and kimchi. Some of these foods may contain live microbes at levels that potentially provide health benefits, but if the fermentation process is done at home, it is hard to ensure the same consistent strain types at sufficiently high numbers to guarantee a health benefit. After the initial fermentation, some fermented foods are further processed (by pasteurisation, baking, or filtering) so they are no longer sources of live microbes. Although fermented foods may be good to consume as part of a healthy lifestyle, the number of benefits cannot be guaranteed as they may not meet the criteria of a probiotic.
Why are they important?
When the digestive tract has an unhealthy balance of bacteria it can compromise our health. Therefore, fermented and probiotic foods can be beneficial by maintaining a healthy balance of microbes. Yakult can help to replenish the beneficial bacteria in our gut and is classified as a probiotic. We use a well-researched strain and test the levels of live bacteria after fermentation to guarantee high numbers in the final product.