Probiotics are a term you have likely heard most often associated with gut health, but you may not be fully aware of what they are or how they support overall health and wellbeing. This article provides a simple introduction to probiotics, including their role, health benefits, food sources, and why including them in a balanced diet can help support a healthy gut.
What are probiotics?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines probiotics as:
“Live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host” (1).
Your digestive system is home to a large and diverse community, comprised of more than 100 trillion microorganisms, including many types of bacteria that work together to support digestion and overall health (2, 3).
What are the health benefits of probiotics?
Probiotics play a key role in gut health by supporting the balance of bacteria within the digestive system (2, 4). More specifically, probiotics may help to:
- Promote regular bowel movements (2, 5)
- Enhance nutrient absorption (6)
- Keep harmful bacteria under control (4)
- Reduce the risk of diarrhoea caused by antibiotics (2)
- Alleviate symptoms associated with digestive issues such as inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS) (2, 7)
- Improve lactose digestion in individuals with lactose intolerance (8)
- Reduce total cholesterol (9)
Why is a healthy gut important?
Maintaining a balanced and healthy gut is essential to support many bodily functions, including:
- The production of important nutrients such as vitamins C, K and B-group vitamins (10)
- Aiding in the digestion of indigestible carbohydrates, also known as prebiotics, which help feed and support the growth of beneficial bacteria (11)
- Supporting immune system health by limiting the overgrowth of potentially harmful microorganisms (2, 4)
Breaking down probiotics:
Probiotics are classified by their three-part name, which comprise of the genus, species, and strain (5) [Figure 1]. However, it is important to note that not all probiotics will provide the exact same health benefits, as the effects are strain specific (5, 12).
Strain specific means that:
- Different probiotic strains have scientific research supporting different health benefits (5)
- The benefits observed in one strain cannot be generalised to another strain, even if they belong to the same genus and species (5)
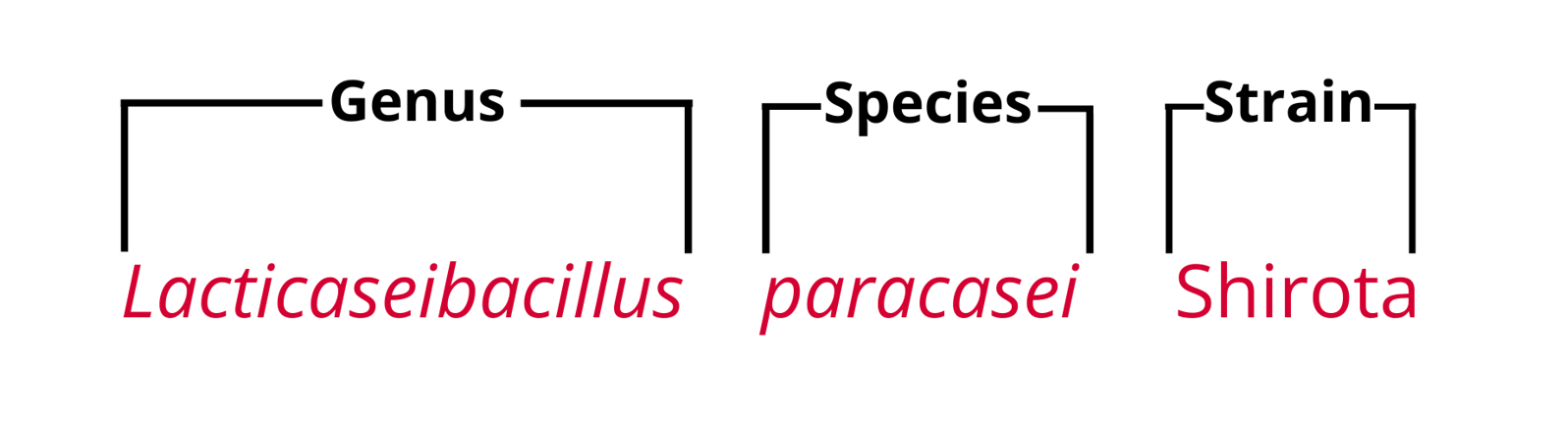
Figure 1. 3-part name of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Shirota strain (LcS)
Where can you find probiotics?
Probiotics can be found in a wide variety of fermented foods, drinks and supplements including (2, 13, 14):
- Cultured buttermilk
- Yoghurt
- Cheese
- Kefir
- Kombucha
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Pickles
- Miso
- Yakult
However, not all fermented foods are probiotics, but rather a live culture, and they cannot automatically be deemed a ‘probiotic’ unless the strains contained have been studied and shown to confer a health benefit.
What is special about Yakult’s Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Shirota (LcS) strain?
Yakult is the only product in the world to contain the unique probiotic bacteria: Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Shirota strain (LcS) and is backed by over 90 years of clinical research supporting its benefits and effectiveness (5).
The key evidence-based benefits of the LcS strain include:
- It can survive through the digestive system to reach the intestines alive (5)
- It can positively alter and increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines (5)
- It can inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria, thereby supporting a balanced gut (5)
- It can encourage regular bowel movements by improving stool consistency (5)
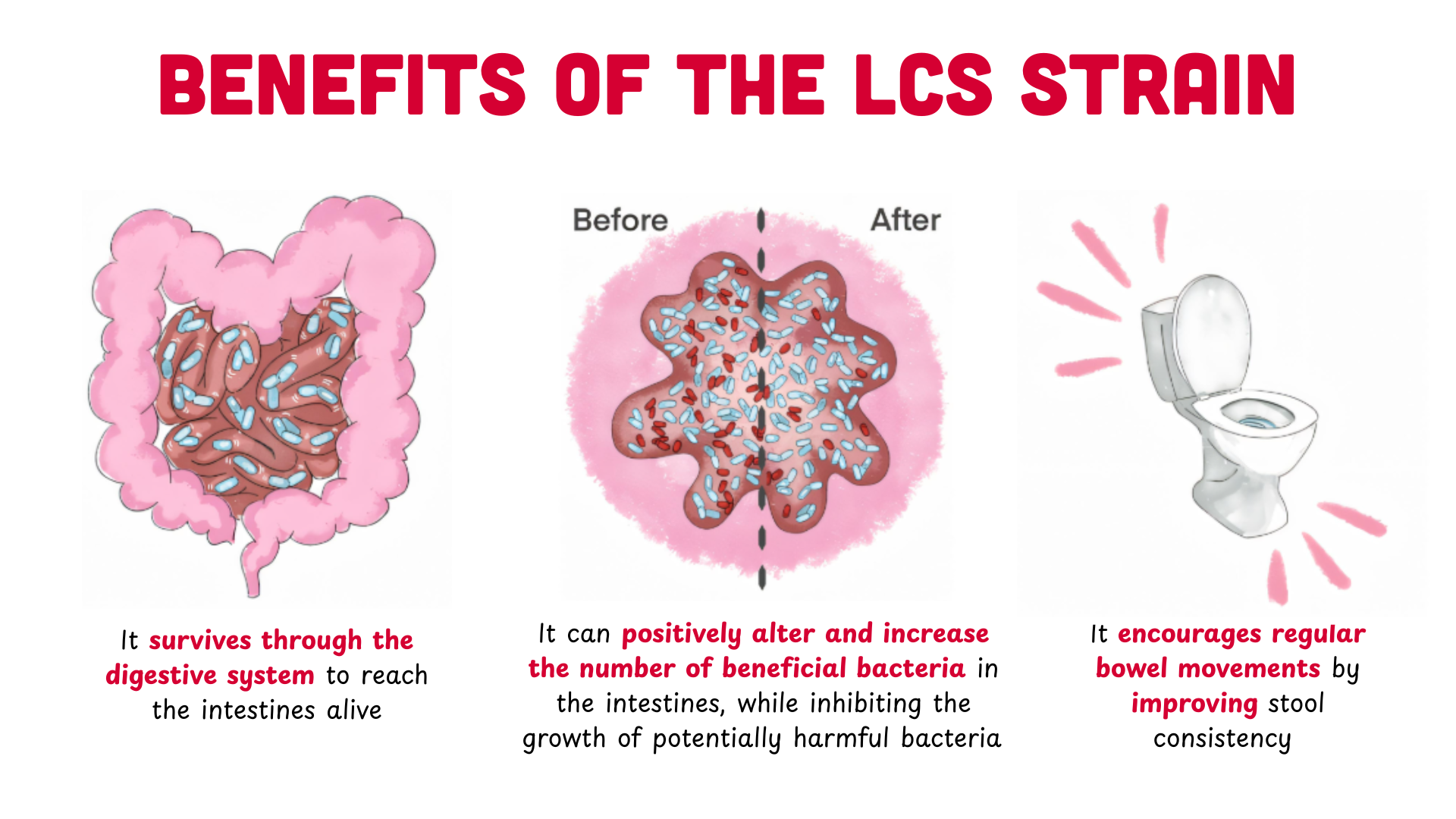
Figure 2. Key benefits of the LcS Strain
If you are unsure of what type of probiotic may be suitable for you, it is recommended to consult an Accredited Practising Dietitian (APD) or your general practitioner to determine whether probiotic consumption is appropriate for your individual needs (2).
References
- Gul S, Durante-Mangoni E. Unraveling the puzzle: Health benefits of probiotics—A comprehensive review. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):1436.
- Healthdirect Australia. Probiotics [Internet]. Canberra: Healthdirect Australia; 2024 [cited 2025 Nov 21]. Available from: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/probiotics
- Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M, Franceschi F, Miggiano GAD, Gasbarrini A, et al. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms. 2019;7(1):14.
- Bhutada S. A comprehensive review of probiotics and human health: Current perspectives and applications. J Food Biochem. 2024;48(1):e11743.
- Yakult Australia. Benefits of probiotics [Internet]. Sydney: Yakult Australia; 2024 [cited 2025 Dec 4]. Available from: https://www.yakult.com.au/benefits/
- Nami Y, Barghi A, Shahgolzari M, Salehian M, Haghshenas B. Mechanism of Action and Beneficial Effects of Probiotics in Amateur and Professional Athletes. Food Sci Nutr. 2025;13(1):e4658. doi:10.1002/fsn3.4658.
- Khatun R. Probiotic drinks: Balancing the benefits with possible side effects. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2024;20(4):1–9.
- Gul S. Unraveling the puzzle: Health benefits of probiotics—A comprehensive review. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):1436.
- Jiang J, Xu Y, Li J, Yuan L. Effects of probiotic supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020;38:82–90.
- Fujisaka S. The gut microbiome: A core regulator of metabolism. J Endocrinol. 2023;256(3):1–15.
- Rabot S, Rafter J, Rijkers GT, Watzl B, Antoine JM. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: impact of probiotics on digestive system metabolism. J Nutr. 2010;140(3):671S–676S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.113738.
- Ganguly NK, Bhattacharya SK, Sesikeran B, Nair GB, Ramakrishna BS, Sachdev HPS, et al. ICMR-DBT guidelines for evaluation of probiotics in food. Indian J Med Res. 2011;134(1):22–25.
- Syngai GG, Gopi R, Bharali R, Dey S, Lakshmanan GMA, Ahmed G. Probiotics: The versatile functional food ingredients. J Food Sci Technol. 2016;53(2):921–933.
- Obayomi OV, Olaniran AF, Owa SO. Unveiling the role of functional foods with emphasis on prebiotics and probiotics in human health: a review. J Funct Foods. 2024;119:106337. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2024.106337.